As we dive into 2026, science is already delivering mind-bending discoveries that feel straight out of sci-fi. From gentler gene editing to fusion power milestones and clues about our ancient cousins, these early-year breakthroughs remind us why facts have stories worth telling. Here are 10 of the most exciting developments making waves right now—each one reshaping our understanding of medicine, energy, human history, and the future of computing.
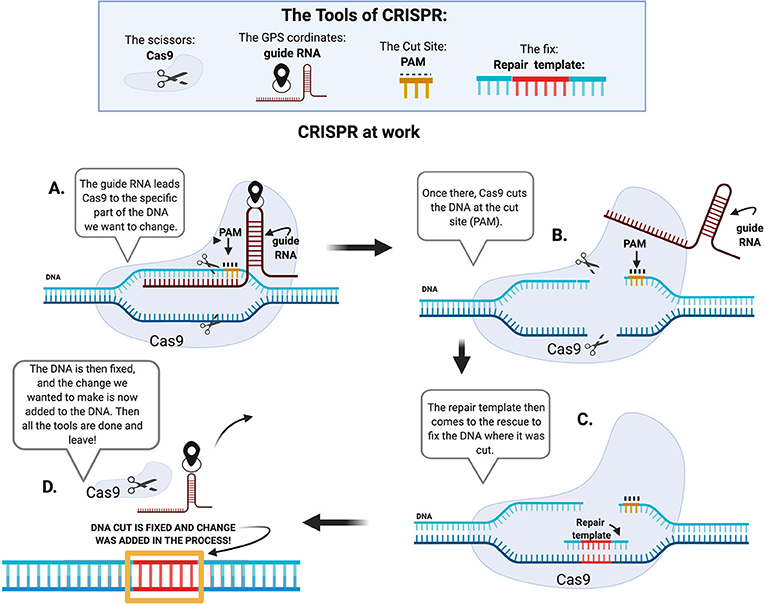
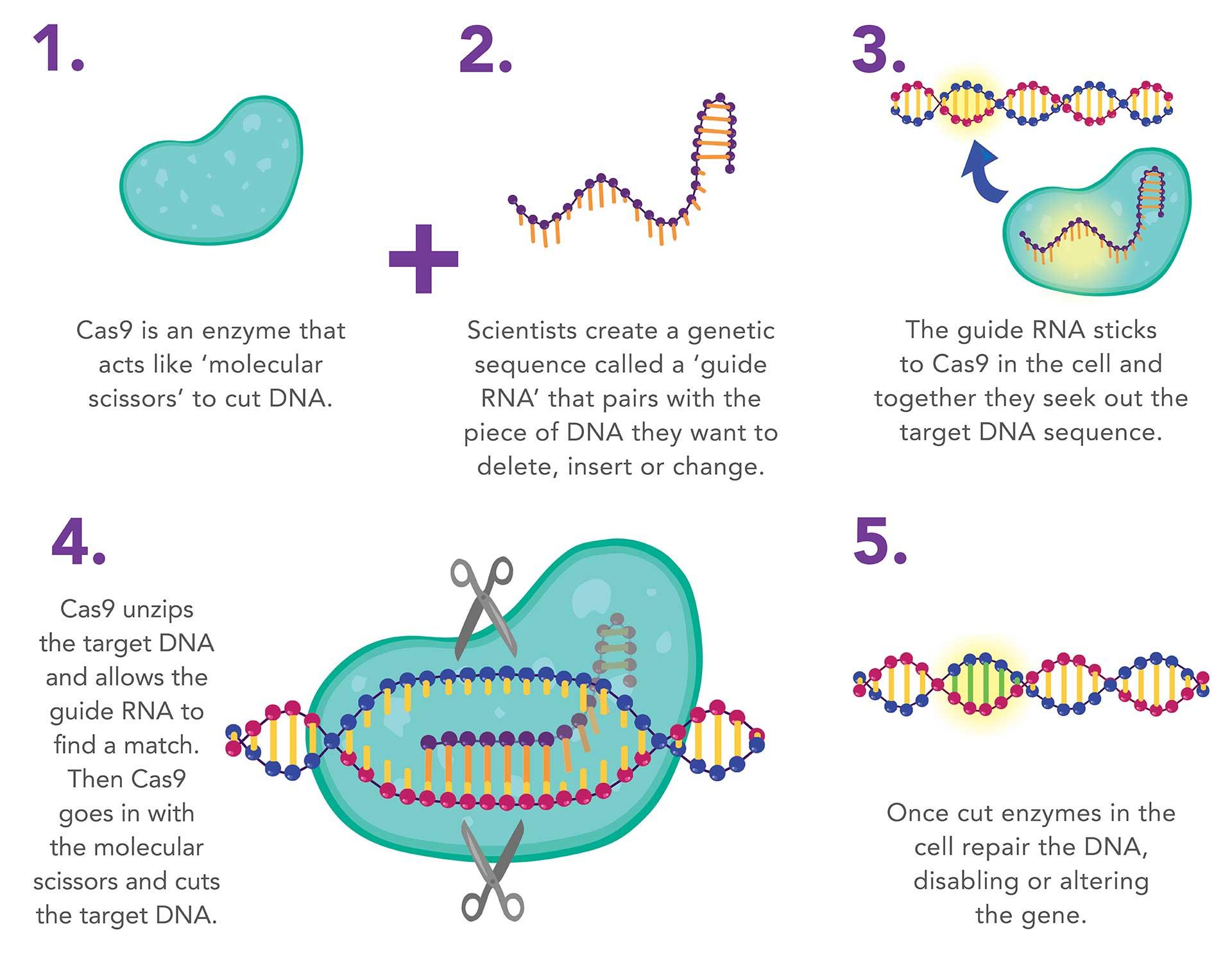
1. CRISPR Goes Gentle: Turning Genes “On” Without Cutting DNA
Scientists have unveiled a revolutionary CRISPR technique that reactivates silenced genes by removing chemical “tags” (epigenetic marks) instead of slicing DNA. This safer approach could treat diseases like sickle cell by reviving fetal hemoglobin—without the risks of traditional edits.

2. China’s “Artificial Sun” Smashes a Fusion Barrier
The EAST tokamak just achieved stable plasma at extreme densities—proving a long-thought “unbreakable” limit can be overcome. This density-free regime keeps fusion reactions steady even as fuel ramps up, bringing clean, limitless energy closer to reality.

3. Neanderthals: New Clues from 2025-2026 Discoveries
Fresh reconstructions and analyses reveal Neanderthals practiced cultural butchering techniques, extracted bone marrow early, and may have had varied diets including insects. These findings paint them as sophisticated hunters and survivors—not the brutish stereotypes of old.


4. Shape-Shifting Molecules: The Dawn of Molecular AI Hardware
Researchers have created dynamic molecules that switch between memory, logic, and learning roles—physically encoding intelligence. This “intelligent matter” could revolutionize computing, moving beyond silicon to brain-like efficiency.


5. Brain-Inspired AI: Breaking Free from Massive Data Needs
For years, the mantra in artificial intelligence has been “bigger is better”—throw more data and compute at models to make them smarter. But early 2026 research from Johns Hopkins University is flipping that script. Scientists redesigned AI architectures to more closely mimic biological brains, and astonishingly, some untrained models started producing activity patterns eerily similar to real human and primate brains when shown images.

This breakthrough challenges the data-hungry paradigm dominating AI development. By prioritizing brain-like structures—such as hierarchical processing and specific connectivity patterns—these models achieved brain-level performance without billions of training examples. Lead researcher Mick Bonner noted that evolution honed efficient learning over millions of years; perhaps we’ve been overcomplicating things with brute-force scaling.
The implications are huge: lower energy costs, faster training, and more accessible AI for resource-limited applications. As neuromorphic (brain-inspired) hardware advances, 2026 could mark the shift toward efficient, biologically grounded intelligence—potentially accelerating fields like robotics and edge computing.
6. Gut Bacteria Swaps Reshape Brain Development in Primates
Your gut microbes might influence your brain more than you think—and new 2026 research shows they could even play a role in primate evolution. Northwestern University scientists transplanted gut bacteria from humans, squirrel monkeys (large-brained), and macaques (smaller-brained relative to body size) into germ-free mice. The results? The mice’s brains began shifting gene expression and function toward patterns matching the donor primates.
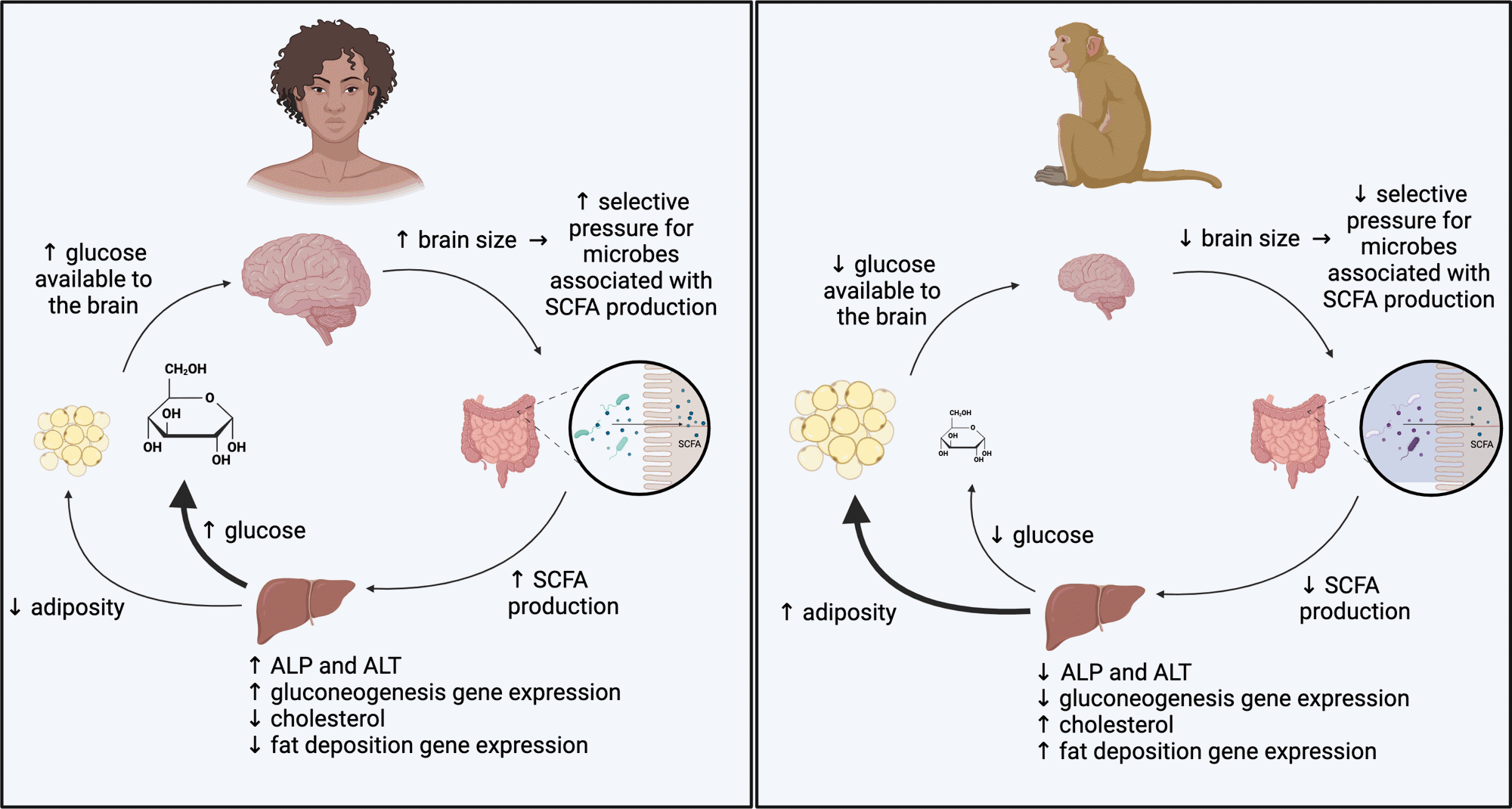

Mice with large-brain primate microbes showed boosted energy metabolism and synaptic plasticity (key for learning). Those with smaller-brain microbes displayed patterns linked to neurodevelopmental conditions like autism and ADHD. This suggests gut microbes help allocate energy to support bigger brains—a metabolic tradeoff that may have driven human evolution.
The gut-brain axis isn’t new, but this is the first direct evidence microbes causally shape neurodevelopment across species. It opens doors to microbiome therapies for brain health and raises questions about early-life microbial exposure in humans.
7. NASA Satellite Reveals Tsunamis Are Far More Complex Than We Thought
Tsunamis have long been modeled as single, coherent waves racing across oceans. But in early 2026, NASA’s SWOT satellite captured the first high-resolution view of a massive Pacific tsunami (triggered by a Kamchatka quake), shattering that simplicity.

Instead of one clean front, the data showed braided, scattered energy with “edge waves” trapped along shelves—persisting for hours. This complexity means current forecasts may underestimate coastal risks. SWOT’s wide-swath radar is revolutionizing ocean observation, promising better warnings and refined models incorporating dispersion.
8. Deep-Sea Quakes Trigger Giant Antarctic Plankton Blooms
The Southern Ocean hosts some of Earth’s largest phytoplankton blooms, vital for carbon sequestration and marine food webs. A December 2025 study (published early 2026) linked their variability to an unlikely source: underwater earthquakes.
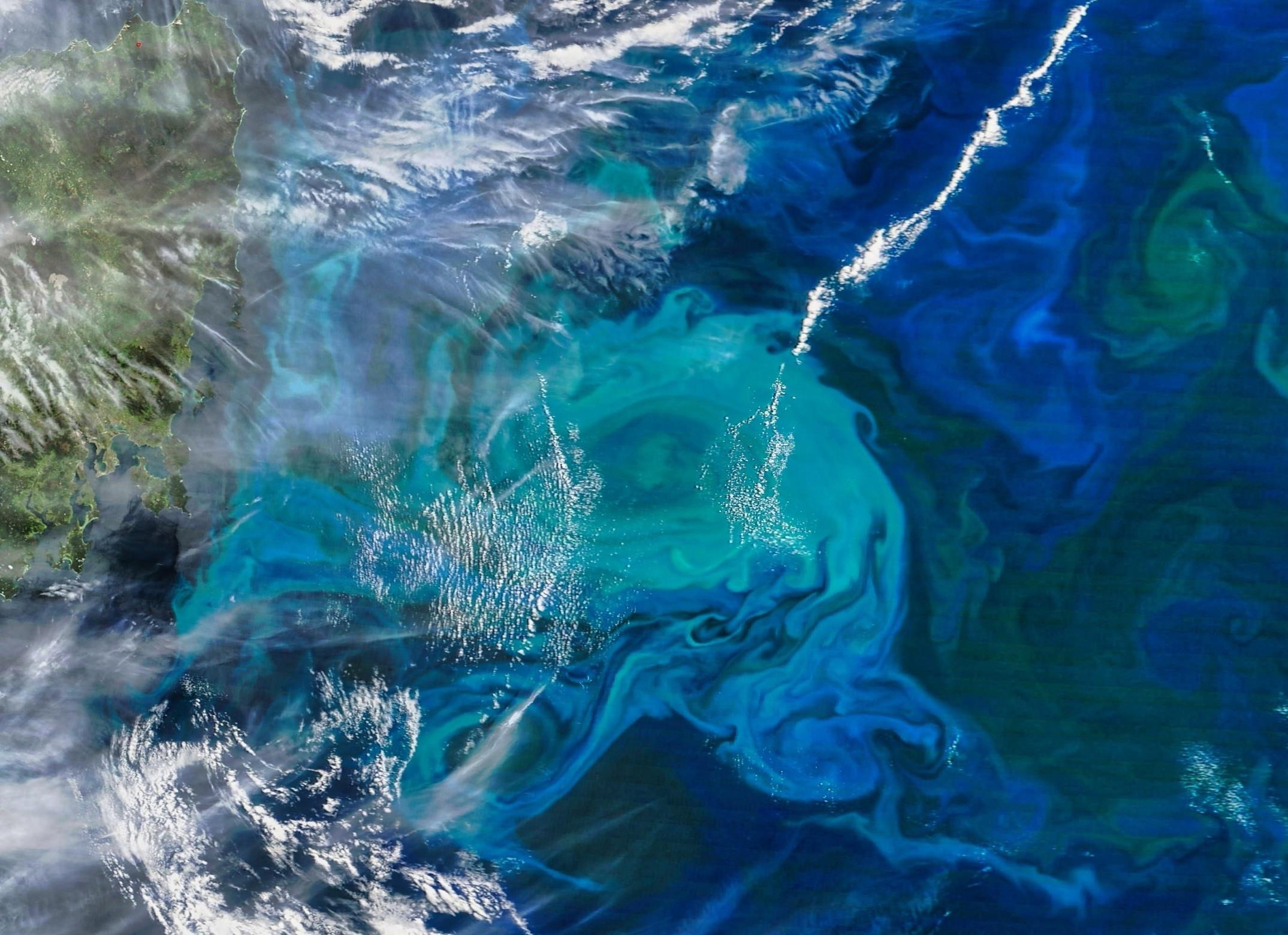


Stanford researchers found magnitude 5+ quakes along the Australian Antarctic Ridge shake hydrothermal vents, releasing iron-rich plumes that fuel summer blooms. Stronger winter seismicity led to denser, more productive blooms—spanning areas the size of California. This deep-to-surface connection highlights Earth’s interconnected systems and seismic influences on climate-regulating biology.
9. CAR T-Cell Therapy Rejuvenates Aging Guts
CAR T-cells, famous for cancer treatment, are now targeting aging. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory researchers used anti-uPAR CAR T cells to clear senescent cells in mouse intestines, reversing age-related decline.


Treated mice showed faster regeneration, reduced inflammation, better nutrient absorption, and protection from radiation damage—effects lasting a year. Human intestinal cells responded similarly. This could combat leaky gut in elders and cancer patients, extending immunotherapy to longevity.
10. Microbes Turn Martian Soil into Building Bricks
Building on Mars means using what’s there. Early 2026 research explores biocementation: tough microbes binding Martian regolith simulant into sturdy, concrete-like material—while potentially producing oxygen as a bonus.
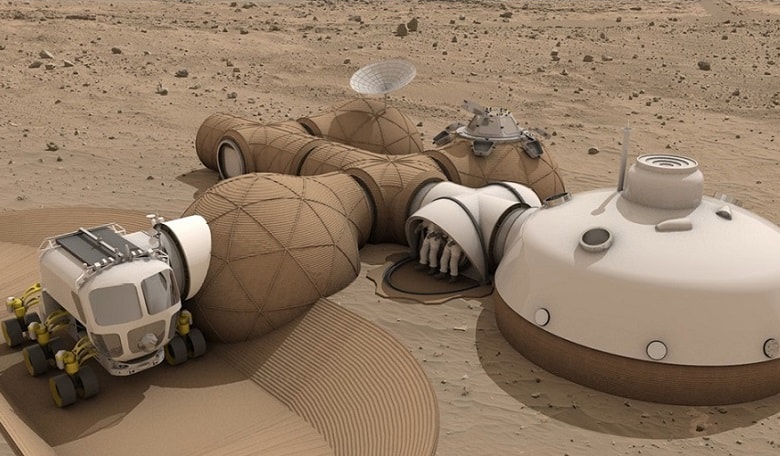
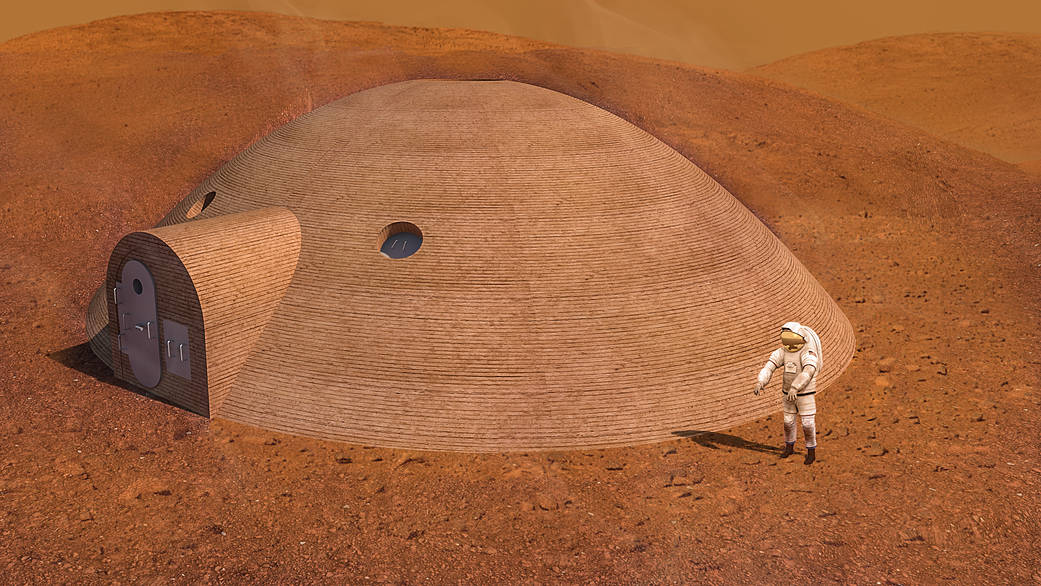
Combined with 3D printing (tested in NASA’s challenges), this in-situ approach slashes transport costs. Microbes induce calcium carbonate precipitation, creating biocement strong enough for habitats. It aligns with sustainable, self-replicating construction for future colonies.
These deeper dives reveal 2026’s science isn’t just incremental—it’s rewriting rules across biology, AI, oceans, and space. Which one sparks your curiosity most? Stay tuned; the year is young! Because facts have stories, and they’re unfolding fast.